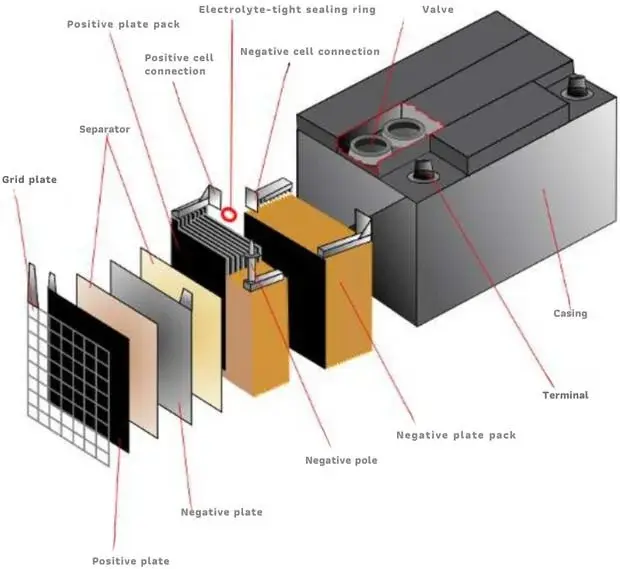
HOW IT IS MADE: THE LEAD ACID BATTERY – PART 2 CONSTITUENT PARTS OF THE BATTERY
- Container: usually made of plastic, it contains a specific concentration of sulphuric acid used in Lead Acid batteries.
- Positive plates are parts of a lead acid battery. There can be just one single plate. However, usually, there are groups of plates. These plates are linked together using electrical connections.
- Negative plates: There can also be many plates in this situation. These plates are connected to each other.
- Separators: partitioning material that prevents physical contact between plates of opposite sign, without preventing the ionic exchange.
Plates of the lead acid battery
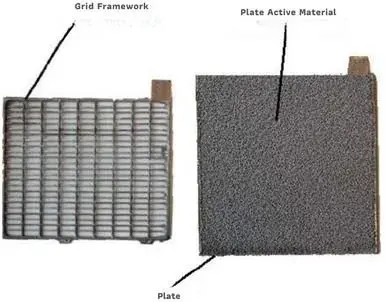
The lead-acid battery plates are submerged in a liquid known as acid. In this setup, the positive and negative plates alternate in a specific sequence. Leaning on grids for support, the lead acid within these batteries plays a crucial role in facilitating the necessary electrochemical reactions. Moreover, the grids serve a dual function: they not only provide mechanical support to the active material but also conduct the resulting electrons during the delivery phase, which are essential for the electrochemical reaction in the charging phase. As a result, each individual plate can achieve a capacity of approximately 10 Ah, contributing to the overall performance of the battery.
In the case of the lead accumulator, the active materials with a charged battery are:
- sulphuric acid (density 1.28 kg/l)
- spongy metallic lead: porous grey mass tending to light blue
- lead dioxide: brownish-reddish porous mass for positive plates
Grids are often made from a material called lead alloy. A lead alloy is a mixture of lead and other metals. Grids need to meet two important requirements. You can see these requirements in the diagram.
- The material is strong enough for people to pick it up and move it around. It won’t break easily when you handle it. This means you can work with it without worrying about damage.
- resistance to the corrosive effect produced by sulphuric acid.
Separators
The lead acid battery plates sit in a liquid called acid. Acid is a strong liquid that can react with other materials. They put the plates in a specific order. The order goes positive, negative, positive, negative. Opposite sign plates cannot be in contact with each other; otherwise, the electric current would pass directly between them without going through the external circuit, causing the so-called short-circuit. With separators dividing the plates, lead acid batteries ensure safe operations. These separators are sheets or envelopes. The purpose of the strips is to wrap one type of plate. The plate can be either positive or negative.
The material used must have specific characteristics:
- resistance to sulphuric acid.
- The material is strong. You can hold it without ripping. This is because it has enough mechanical strength. Mechanical strength means the ability to withstand forces without breaking.
- low resistance to the ionic exchange between the electrodes while still providing physical insulation between them.
To stay updated with the latest developments in STEM research, visit ENTECT Online. This is our digital magazine for science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
/how-it-is-made-the-lead-acid-battery-part-x-assembly





