How it is Made: The Lead Acid Battery – Part IX DRY CHARGE
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Batteries in the market are divided into two main families: ‘wet charged’ batteries and ‘dry charged’ batteries. Wet charged batteries consist of positive plates, negative plates, and electrolyte.
What are Dry Charged Lead Acid Batteries?
Dry charged batteries contain plates in the physical state of a charged battery (+PbO2 – Pb), but there is no electrolyte. Now, you might be wondering, what does “dry charged” mean? Well, in a typical lead acid battery, the acid solution keeps the lead plates moist to produce electricity. However, in a dry charged battery, the plates remain dry until the battery is ready for use. At that point, we add the acid, and the battery springs to life. Dry charged lead acid batteries have a longer shelf life. They can be stored for a long time. They do not lose their charge.
How Do They Work?
The magic of dry charged lead acid batteries lies in their chemistry. When the sulfuric acid solution is added to the battery, it reacts with the lead plates. This produces lead sulfate and water. This reaction releases electrons.
These electrons flow out of the battery and provide electrical power.
We need this power to run our devices. When the battery is recharged, the lead sulfate and water are converted back into lead and sulfuric acid. The battery is ready to start the process all over again.
Manufacturing of Dry Charged Lead Acid Batteries
The steps required to manufacture a dry charged battery are:
1. Charging of the Plate
2. Drying Process
Charging the Plate
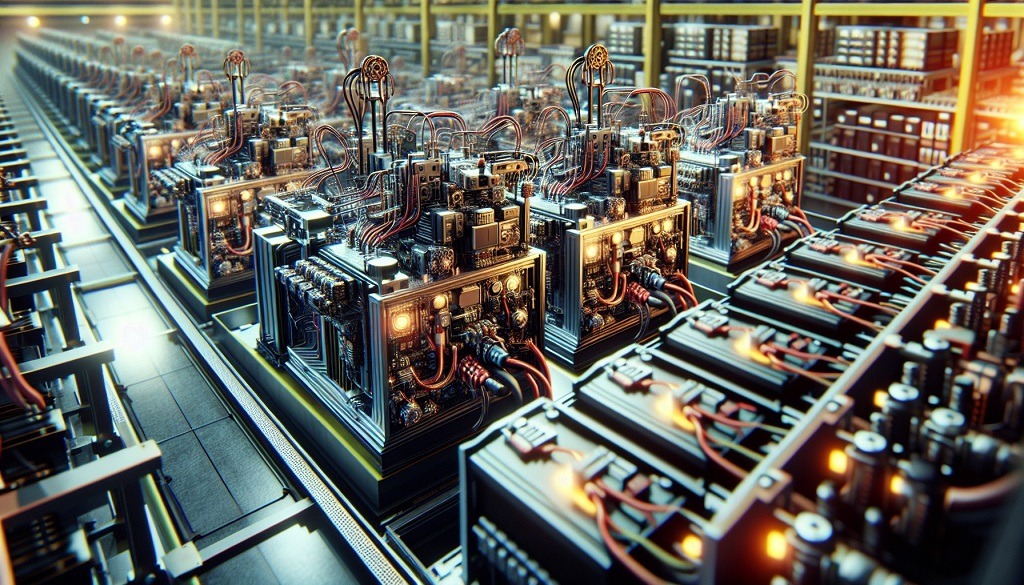
Once the curing process has been completed, the following elements compose the resulting plate: Pb+PbO+PbO2 +H2O+PbSO4+Grid+ Additives. It is therefore necessary to charge the plate by turning the amorphous matter of the plate into active material.
To do this, one must form large groups of plates and immerse them in large tanks filled with electrolyte. Then, pass the electrical current required for transforming the active material (380-450 A/kg) through them to charge the dry lead acid batteries.
The charging current will be supplied by single channel rectifiers. There is a specific option to reverse the charge polarity on the battery power cables. This specificity allows for the connection of the plates to the electrodes without the need for manual welding operations. The charge currents will be delivered according to a counter-electromotive force coming from the plates.
At the end of the forming phase the active material constituting the electrodes is in a particular physical condition. The positive will consist of lead dioxide (PbO2), the negative will consist of metallic lead (Pb).
Drying Process
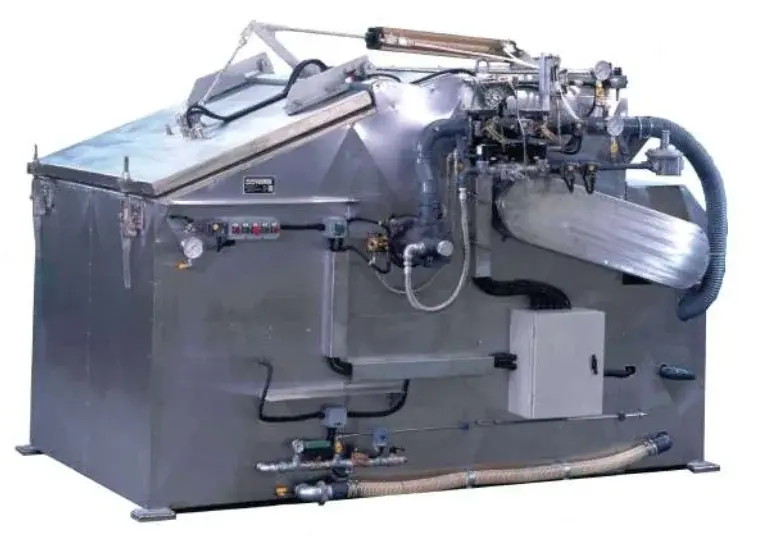

The two plates (positive and negative) must undergo a drying process before being suitable for use to manufacture the battery. A stream of hot air can dry the positive plate. Metallic lead makes the negative plate. It will need a drying treatment in an oxygen-free environment. Metallic lead, impregnated with electrolyte, might easily come out due to violent oxidation. This could lead to the melting of the plate itself. A specific machine obtains the drying. The machine has an appropriate heating system. This system allows the elimination of oxygen in the combustion phase.
Drying and condensation cycles extract moisture from the plate, depositing it in an unloading area, essential steps in handling dry charged lead acid batteries.
Applications of Dry Charged Lead Acid Batteries
Dry charged lead acid batteries have a wide range of applications. Commonly used in cars, motorcycles, and other vehicles, they provide the initial power to start the engine. They also use them in emergency lighting systems, alarm systems, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, which provide reliable backup power in case of a power outage.
Advantages of Dry Charged Lead Acid Batteries
There are several advantages to using dry charged lead acid batteries. First, as we mentioned earlier, they have a long shelf life. Manufacturers and retailers benefit from the ability to store them for a long time without losing their charge. Second, they are relatively inexpensive to produce, which makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications. Third, they are capable of delivering a high surge of power, which is necessary for starting engines and other high-power applications.
Disadvantages of Dry Charged Lead Acid Batteries
Dry charged lead acid batteries also have some disadvantages. One of the main ones is that they are quite heavy, which can be a drawback for portable applications. They also have a relatively short cycle life, which means they need replacing more often than some other types of batteries. Finally, they contain lead and sulfuric acid, which are harmful to the environment and require proper disposal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dry charged lead acid batteries are a key part of our modern world, powering everything from cars to emergency lighting systems. While they have some drawbacks, their advantages make them a popular choice for many applications.
So next time you start your car or see a UPS system in action, remember the humble lead acid battery that makes it all possible!
Thanks for reading!
Additionally, to stay updated with the latest developments in STEM research, visit ENTECH Online. Basically, this is our digital magazine for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Furthermore, at ENTECH Online, you’ll find a wealth of information.






