Nitrogen Containing Compounds in Pharmacy
The element was discovered in 1772 by the Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford. Initially, it was referred to as “noxious air” or “fixed air,” as Rutherford found it was a component of air that did not support combustion or life. Over time, scientists began to understand the inert properties of nitrogen gas, knowing its potential in various fields, including chemistry and medicine. Nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements on Earth, has significantly emerged in the pharmaceutical industry. Its unique properties and applications make it essential element in drug design and production. This article delves into nitrogen’s position and characteristics on the periodic table, nitrogen containing compounds and their impact on the pharmaceutical industry. Further, we will discuss the challenges and future prospects associated with its use.
Position and Characteristics of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a non-metallic element having the symbol ‘N’ and has an atomic number of 7. It belongs to group 15 of the periodic table, often referred to as the pnictogens. Moreover, nitrogen typically exists as a diatomic molecule (N₂), which is a colorless and odorless gas at room temperature. Key characteristics include:
- Atomic Number: 7
- Atomic Mass: 14.007 amu
- Electron Configuration: [He] 2s² 2p³
- Melting Point: -210 °C [-346°F]
- Boiling Point: -195.795 °C [-320.431°F]
- Density: 1.2506 g/L at STP
These properties make nitrogen highly inert, which is crucial for various applications in medicine where reactive gases can compromise product integrity and safety.
Pioneering Utilization in Pharmaceuticals
One of the first significant utilizations of nitrogen in drug development was in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with the synthesis of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. Particularly, heterocycles are ring structures containing nitrogen atoms and are fundamental in medicinal chemistry.
Classification of Nitrogen Containing Compounds
The table below gives the names, classification and properties of drugs containing nitrogen in their structures. Also, these structures are called heterocycles of nitrogen.
On the basis of their properties, nitrogenous drugs are classified as follows:
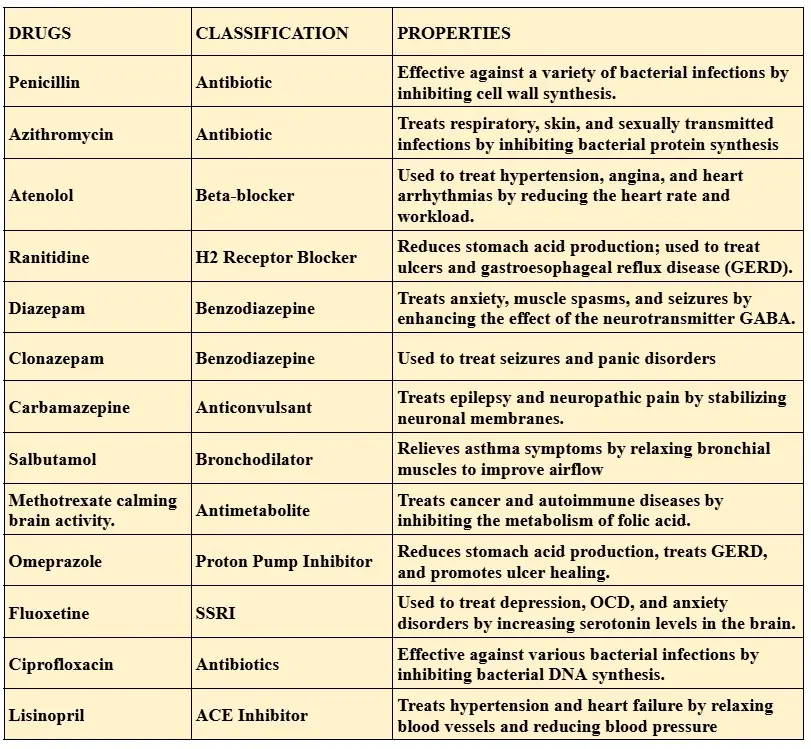
Notable Milestones
- 1900s: Paul Ehrlich, a scientist, used nitrogen containing compounds for the development of the first chemotherapy drug, Salvarsan, for treating syphilis. Therefore, this marked the beginning of the targeted use of nitrogen in pharmacology.
- 1920s: Discovery of sulfa drugs, another class of antibiotics, which were the first to contain sulfur and nitrogen atoms, revolutionizing bacterial infection treatment.
- 1940s: The discovery and subsequent mass production of penicillin, a nitrogen-containing antibiotic, which became a game changer in treating bacterial infections and saving countless lives during World War II and beyond.
These early discoveries showcase the immense potential of nitrogen in enhancing the efficacy and stability of pharmaceutical compounds.
Nitrogen’s Role in Pharmaceutical Industry

The legacy of these early discoveries paved the way for nitrogen to become a crucial building block in numerous modern drugs. Eventually, today, nitrogen atoms are found in a myriad of pharmacy, ranging from antibiotics and analgesics to anticancer agents and beyond.
- Drug Design and Synthesis: Nitrogen-containing compounds are building blocks in many pharmaceuticals. Compounds like penicillin, cephalosporins, and alkaloids owe their efficacy to nitrogen atoms within their structures. Also, its ability to form stable bonds with multiple elements enhances the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs.
- Manufacturing and Storage: Nitrogen is used widely to create inert atmospheres during drug production. This helps in preventing oxidation of sensitive compounds. For example, it is used in the purging and blanketing of storage containers to maintain sterility and extend shelf life.
- Sterilization and Packaging: Nitrogen finds use in sterilization processes, to make sure that medicine is free from microbial contamination. Additionally, in packaging, nitrogen displaces oxygen, reducing the risk of degradation and maintaining product efficacy.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Challenges:
- Purity Standards: Specifically, reaching ultra-high purity nitrogen is vital, as contaminants can affect drug quality.
- Cost: The generation and maintenance of high-purity nitrogen can be cost-prohibitive for smaller pharma companies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent regulatory standards across different regions, eventually adds complexity to nitrogen containing compounds and their use in pharmaceuticals.
Future Prospects:
- Advancements in PSA Technology: Also, Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology for nitrogen generation promises improved purity and cost-effectiveness.
- Nitrogen Application in Advanced Therapies: As pharmaceutical research progresses, nitrogen’s role in new drug modalities, such as biologics and gene therapies, will expand.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of nitrogen production and use will gain momentum, consequently aligning with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Nitrogen has proven to be an unbeatable player in the pharmaceutical industry. Ranging from its critical role in drug development to its application in manufacturing and storage processes. Its unique position on the periodic table, coupled with its chemical properties, makes it an important element in many life-saving medications. Despite the challenges associated with achieving high purity levels, regulatory compliance, and cost management, the future prospects of nitrogen in pharmaceuticals remain promising. Advancements in technology and sustainable practices will continue to enhance its utility. Further, Nitrogen Containing Compounds catalytic role in driving innovation underscores its importance. Therefore, it remains a pivotal element in the quest for new and effective therapies.
References
- Heravi, M. M., & Zadsirjan, V. (2020). Prescribed drugs containing nitrogen heterocycles: an overview. RSC Advances, 10(72), 44247–44311. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra09198g
- Kerru, N., Gummidi, L., Maddila, S., Gangu, K. K., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2020). A review on recent advances in Nitrogen-Containing molecules and their biological applications. Molecules, 25(8), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081909
- Amin, A., Qadir, T., Sharma, P. K., Jeelani, I., & Abe, H. (2022). A review on the medicinal and industrial applications of N-Containing heterocycles. The Open Medicinal Chemistry Journal, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.2174/18741045-v16-e2209010
Additionally, to stay updated with the latest developments in STEM research, visit ENTECH Online. Basically, this is our digital magazine for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Furthermore, at ENTECH Online, you’ll find a wealth of information.






