Polymers: The Invisible Force Shaping Our Everyday Lives
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Polymers are materials that we use for a variety of things in our daily lives. They surround us from the moment we wake up to the moment we go to sleep. These materials consist of molecules with repeating parts. They play an important role in many aspects of daily life and Classification of Polymers, often without our knowledge.
Polymers—those intricate molecular weavings—are everywhere, shaping our daily lives and the very fabric of our existence.
The Building Blocks of Our World

Let’s understand their essence:
What are Polymers?
A polymer is a large molecule or macromolecule, essentially a combination of many subunits. The term “polymer” in Greek means “many parts.” Plants and animals naturally contain polymers, while humans create synthetic polymers. They exhibit unique physical and chemical properties, making them indispensable in everyday life.
Classification of Polymers
Based on Source of Availability
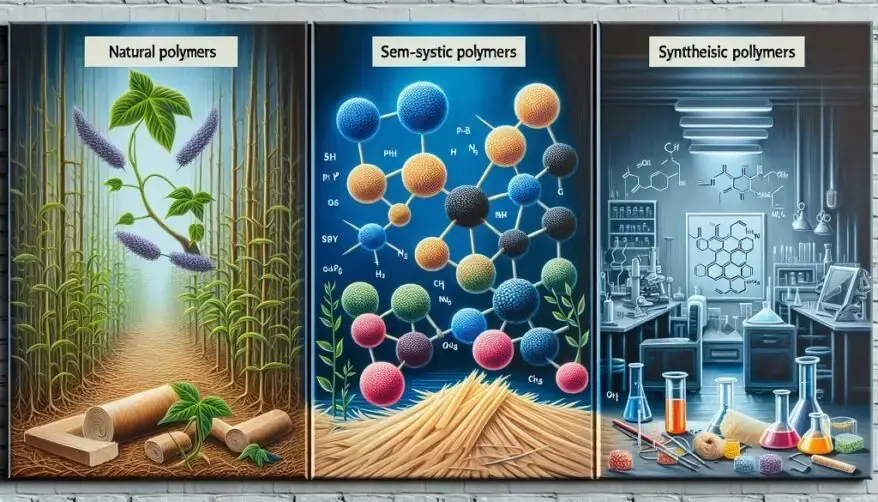

- Natural: Occur naturally in plants and animals (e.g., proteins, starch, cellulose, and rubber).
- Semi-synthetic: Derived from naturally occurring polymers and undergo further chemical modification (e.g., cellulose nitrate).
- Synthetic: Human-made (e.g., plastics like nylon).
Based on Structure of Monomer Chain
- Linear: Long, straight chains (e.g., polyvinyl chloride for pipes).
- Branched-chain: Linear chains with branches (e.g., low-density polyethylene).
- Cross-linked: Form 3D networks (e.g., rubber).
- Network: Highly cross-linked (e.g., Bakelite).
Polymers: The Unseen Architects
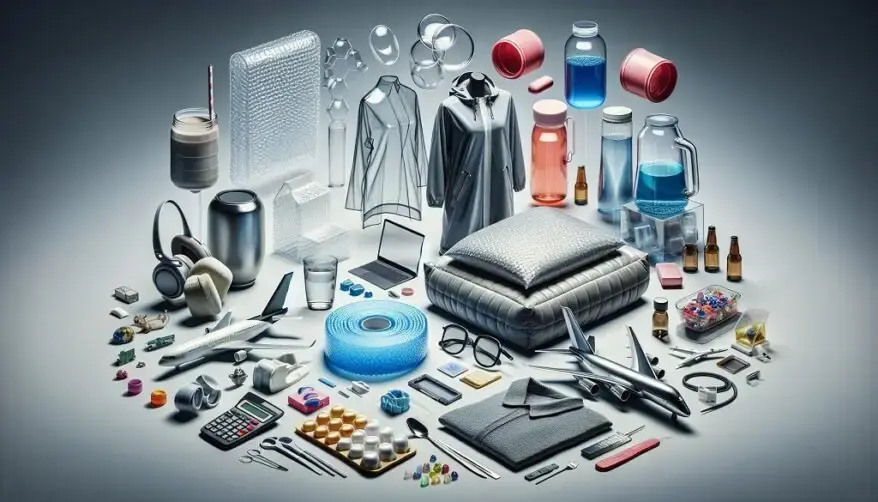

Clothing and Textiles
- Polyester: That favorite T-shirt? Polyester, a polymer that combines durability, wrinkle resistance, and vibrant colors, likely makes up your favorite T-shirt. We weave polyester fibers into fabrics to maintain our comfort and style.
- Nylon: Have you ever wondered about those sleek leggings or sturdy backpacks? Nylon, another polymer, provides strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance. This is the unsung hero behind our activewear and outdoor gear.
- Spandex (Lycra): Yoga pants, swimsuits, and stretchy waistbands owe their flexibility to spandex. This polymer can stretch up to 600% without losing shape—a true marvel of comfort.
Packaging and Food Preservation
- Plastic Containers: The yogurt cup in your fridge? It’s a polymer-based container. Plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) keep our food fresh, prevent leaks, and reduce waste.
- PET Bottles: Those water bottles? Made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), they’re lightweight, shatterproof, and recyclable.
Electronics and Gadgets
- Circuit Boards: Inside your smartphone or laptop, epoxy resins (polymers) hold intricate circuitry together. They insulate, protect, and ensure smooth functioning.
- Insulating Wires: Are the wires transmitting electricity safely? Polymers coat the wires to ensure their safety and flexibility.
Medical Marvels
- Implants: Artificial joints, heart valves, and dental crowns often use biocompatible
- polymers. They integrate seamlessly with our bodies.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Polymers control drug release, ensuring precise dosing and long-lasting effects.
Automotive and Aerospace
- Tires: Rubber, a natural polymer, provides grip, shock absorption, and durability. It’s the unsung hero of road safety.
- Interior Components: Car dashboards, seats, and panels use plastics (polymers) for comfort and aesthetics.
Polymer Chemistry: Crafting Tomorrow’s Innovations
Smart Polymers and Sustainable Solutions
- Smart Polymers: Imagine materials that respond to their environment – temperature, pH, or light. These “smart” polymers hold promise in drug delivery, sensors, and adaptive surfaces.
- Biodegradable Alternatives: Researchers are reimagining plastics. Biodegradable polymers break down naturally, reducing our environmental footprint.
Nanocomposites and 3D Printing Revolution
- Nanocomposites: By blending polymers with nanoparticles, we enhance strength, conductivity, and flame resistance. Nanotechnology and materials science meet!
- 3D Printing: Polymers pave the way for intricate, customized structures, whether in medicine or aerospace.
Career Pathways in Polymer Chemistry

Research and Academia
Pursue a master’s or Ph.D. in polymer chemistry. Unlock doors to cutting-edge research and teaching.
Industry Roles
- Polymer Chemist: Innovate in R&D labs, designing new materials and coatings.
- Formulation Chemist: Create adhesives, paints, and cosmetics using polymer magic.
- Polymer Engineer: Combine chemistry and engineering to create automotive and aerospace breakthroughs.
- Materials Scientist: Explore nanotechnology, biomaterials, and energy storage.
Quality Control and Sustainability
- Quality Assurance: Ensure polymer-based products meet high standards through rigorous testing.
- Environmental Chemistry: Address plastic waste and recycling challenges head-on.
Eco-Smart Moves: Boosting Polymer Sustainability
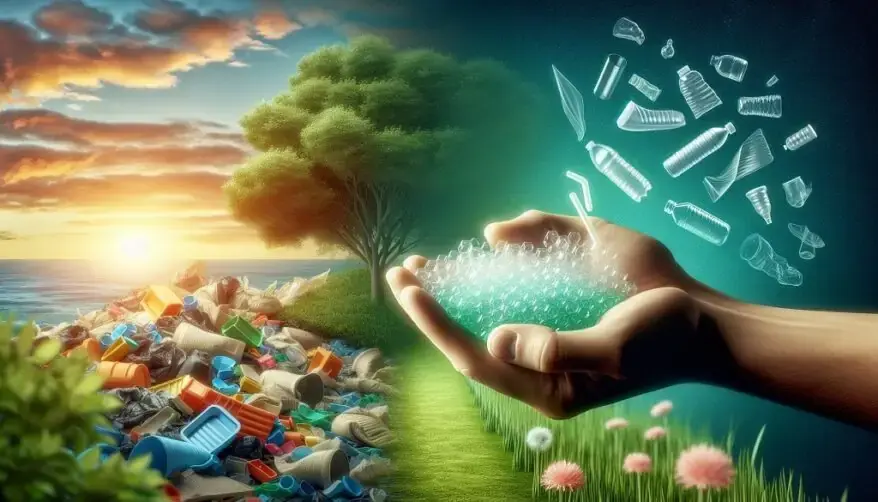

- Green Polymer Synthesis Methods: Researchers explore environmentally friendly approaches to creating polymers, minimizing the use of hazardous chemicals and energy-intensive processes.
- Biodegradable Polymers: Developing materials that naturally break down reduces plastic waste and environmental impact. Biodegradable polymers offer a promising solution.
- Recycling Technologies: Advancements in mechanical, chemical, and biological recycling processes aim to minimize plastic waste. These technologies promote a circular economy.
- Innovative Approaches: Concepts like upcycling and hybrid methods address plastic pollution. They transform waste into valuable resources, contributing to long-term sustainability.
- Challenges and Future Prospects: Researchers and industry professionals must collaborate to drive meaningful change. Eco-friendly practices are essential for a more sustainable polymer future.
Conclusion
Polymers are truly the invisible force shaping our everyday lives. They are important for our daily lives. They are present in the clothes we wear and the devices we use. We use them in food packaging and in our homes. These materials help keep us comfortable, safe, and healthy. Chemistry involves the study and creation of polymers. As this field grows, we will see new and exciting uses for these special materials. The field of polymer chemistry is at an exciting crossroads. On one hand, we grapple with precision, sustainability, and interdisciplinary collaboration. On the other hand, we embrace the promise of smart materials. These are materials that can change their properties in response to their environment.
We also value sequence-defined polymers. These are special types of plastics with a specific order of molecules. Additionally, we welcome the unpredictable evolution of science. Science is constantly changing and evolving in unexpected ways.
As we weave together innovation and responsibility, polymer chemistry shapes a future where molecules hold transformative power.
To stay updated with the latest developments in STEM research, visit ENTECH MAGAZINE. This is our digital magazine for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
At ENTECH, you’ll find a wealth of information. We offer insights and resources to fuel your curiosity. Our goal is to inspire your passion for new scientific discoveries.