Discover Cell Biology: The Foundation of Life Explained
Estimated reading time: 1 minute
Cytology, also known as cell biology, is the branch of science that focuses on the study of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and cytology seeks to understand their structure, function, and interactions. The word “cytology” comes from the Greek words “kytos,” meaning cell, and “logos,” meaning study.
Studying cells is crucial in understanding life itself. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are responsible for carrying out all the processes necessary for an organism to function. By studying cells, scientists can gain insights into how organisms grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis. Cytology also plays a vital role in understanding diseases and disorders, as many diseases originate at the cellular level.
Key Takeaways
- Cytology is the study of cells, which are the basic units of life.
- Understanding cytology is important in comprehending the complexities of life and the functions of different cell types.
- Cell biology techniques, such as microscopy and cell culture, are used to study cells and their functions.
- Cytology has a rich history, tracing back to the discovery of the microscope and the first observations of cells.
- Cytology has important applications in medicine, including diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
The Significance of Cells: Why Cytology is Important in Understanding Life
Cells are considered the basic unit of life because they are the smallest structures capable of performing all the functions necessary for life. They are responsible for carrying out essential processes such as metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli. Without cells, life as we know it would not exist.

Understanding cells is crucial in maintaining life processes. Cells work together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that carry out specific functions in an organism. For example, muscle cells contract to allow movement, while nerve cells transmit electrical signals for communication. By studying cells, scientists can gain insights into how these processes occur and how they can be disrupted in diseases.
Cytology also plays a significant role in understanding diseases and disorders. Many diseases originate at the cellular level, whether it be due to genetic mutations or environmental factors. By studying cells, scientists can identify abnormalities and understand how they contribute to disease progression. This knowledge can then be used to develop diagnostic tests and treatments.
The Building Blocks of Life: Discovering the Wonders of Cell Biology
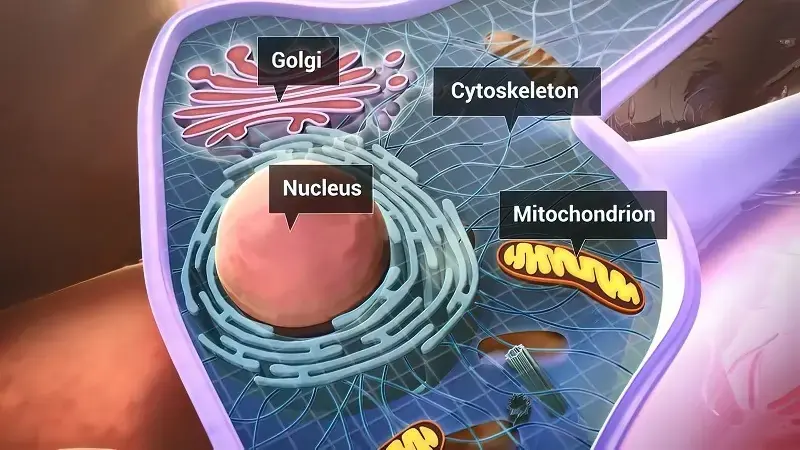
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, are simple in structure and do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells make up all multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
Cells have various structures and functions that allow them to carry out their roles in an organism. The cell membrane acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Organelles, such as the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, perform specific functions within the cell. The cytoskeleton provides structural support and allows for cell movement. These structures work together to ensure the proper functioning of the cell.
Cell processes and interactions are also essential in maintaining life. Cells communicate with each other through chemical signals, allowing them to coordinate their activities. They also undergo processes such as cell division, which is necessary for growth and repair. Cells can interact with their environment through processes like phagocytosis, where they engulf and digest foreign particles.
The History of Cytology: Tracing the Roots of Cell Biology
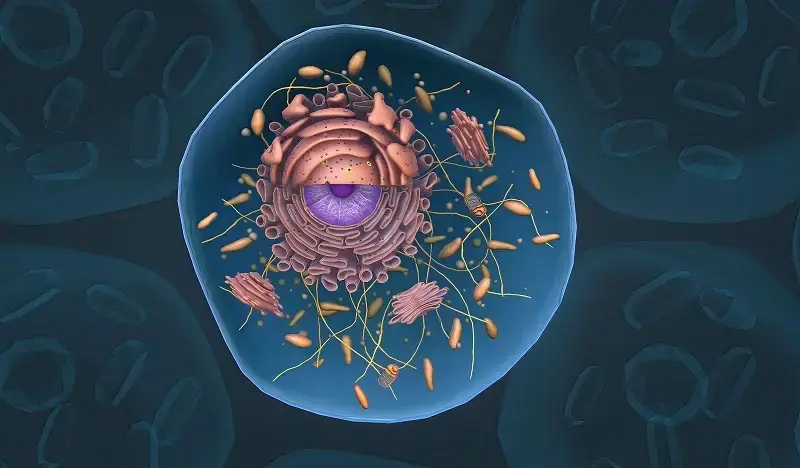
The study of cells dates back to ancient times, with early observations of cells made by ancient Greek philosophers such as Democritus and Aristotle. However, it was not until the invention of the microscope in the 17th century that scientists were able to study cells in detail.
One of the first significant discoveries in cell biology was made by Robert Hooke in 1665. Using a simple microscope, Hooke observed thin slices of cork and described them as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These boxes were later named cells by another scientist, Marcello Malpighi.
In the 19th century, advancements in microscopy allowed scientists to study cells in greater detail. Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed the cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of cells and that cells are the basic unit of life. This theory laid the foundation for modern cell biology.
The field of cytology continued to evolve throughout the 20th century with the development of new techniques and technologies. Scientists such as Albert Claude, Christian de Duve, and George Palade made significant contributions to our understanding of cell structure and function. Today, cytology is a well-established field of study with numerous applications in various scientific disciplines.
The Structure of Cells: Unpacking the Complexities of Cell Anatomy
Cells have a complex structure that allows them to carry out their functions. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates it from its environment. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, ensuring that only certain molecules can enter or exit.
Within the cell, there are various organelles that perform specific functions. The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell because it contains the genetic material, DNA. The DNA carries the instructions for making proteins, which are essential for cell function.
Other organelles include the mitochondria, which produce energy through cellular respiration, and the endoplasmic reticulum, which is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for transport within or outside the cell. Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
The cytoskeleton provides structural support to the cell and allows for cell movement. It is made up of protein filaments called microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. These filaments help maintain cell shape, facilitate cell division, and enable cellular movements such as muscle contraction.
The Function of Cells: Understanding the Roles of Different Cell Types

Different types of cells have specialized functions that contribute to the overall functioning of an organism. For example, muscle cells are responsible for contraction and movement, while nerve cells transmit electrical signals for communication. Epithelial cells line the surfaces of organs and form barriers to protect against pathogens.
Cells can also come together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. Muscle tissue consists of muscle cells and enables movement. Organs are made of various tissues that function together for a specific purpose. The heart is an example of an organ. It includes muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nerve tissue.
Cells also interact with their environment to carry out their functions. They can respond to external stimuli such as light or temperature changes. They can also interact with other cells through chemical signals, allowing them to coordinate their activities.
Cell Biology Techniques: Exploring the Tools and Methods Used in Cytology
Cytology relies on various techniques and tools to study cells in detail. Microscopy is one of the most important techniques used in cell biology. Light microscopy allows scientists to observe cells and their structures using visible light. Electron microscopy, on the other hand, uses a beam of electrons to achieve higher resolution images.
Cell culture is a key technique in cytology. In the lab, cells are grown under controlled conditions. This allows scientists to examine their behavior and properties. Cell culture is utilized in several areas, such as drug development and tissue engineering.
Molecular biology techniques are also widely used in cytology. These techniques allow scientists to study the genetic material within cells and understand how it influences cell function. Techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA sequencing have revolutionized our understanding of genetics and have numerous applications in cell biology.
The Future of Cytology: Innovations and Advancements in Cell Biology Research
The field of cytology is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques being developed. One area of innovation is in imaging techniques, which allow scientists to study cells in greater detail. Super-resolution microscopy, for example, can achieve resolutions beyond the diffraction limit of light, allowing for the visualization of cellular structures at the nanoscale.
Advancements in genetic engineering and molecular biology techniques are also driving progress in cytology. Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 have revolutionized the field by allowing scientists to edit genes with precision. This has opened up new possibilities for studying cell function and developing therapies for genetic diseases.
The emerging field of single-cell analysis is also poised to make significant contributions to cytology. This field focuses on studying individual cells rather than populations of cells, allowing for a more detailed understanding of cellular heterogeneity and function.
The Importance of Cytology in Medicine: Applications in Diagnosis and Treatment
Cytology plays a crucial role in medicine, particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Diagnostic tests such as Pap smears and biopsies rely on the examination of cells to detect abnormalities or signs of disease. For example, Pap smears are used to screen for cervical cancer by examining cells from the cervix for signs of precancerous or cancerous changes.
Cell-based therapies are also becoming increasingly important in medicine. Stem cell therapy, for example, involves using stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues or organs. These therapies hold great promise for treating a wide range of diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and heart disease.
Cytology also plays a crucial role in understanding and treating diseases. By studying cells, scientists can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of diseases and develop targeted therapies. For example, understanding how cancer cells behave and interact with their environment has led to the development of targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy cells.
The Wonders of Cytology: Appreciating the Beauty and Complexity of Life’s Foundation
Studying cytology allows us to appreciate the beauty and complexity of life’s foundation. Cells are incredibly diverse and complex, with each type of cell having its own unique structure and function. From the intricate network of organelles within a eukaryotic cell to the simple yet efficient structure of a prokaryotic cell, cells are truly wonders of nature.
Cells are also responsible for shaping life on Earth. Through evolution, cells have given rise to the incredible diversity of organisms that inhabit our planet. From the smallest bacteria to the largest mammals, all life is composed of cells. By studying cytology, we can gain a deeper understanding of how life has evolved and how organisms have adapted to their environments.
The study of cytology also inspires wonder and awe. The more we learn about cells, the more we realize how little we know. There are still many mysteries to be unraveled, and new discoveries are being made every day. Cytology is a field that constantly pushes the boundaries of our knowledge and challenges our understanding of life itself.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cytology is a fascinating field that seeks to understand the structure, function, and interactions of cells. Cells are the basic unit of life and play a crucial role in maintaining life processes. By studying cells, scientists can gain insights into how organisms grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis. Cytology also plays a vital role in understanding diseases and disorders, as many diseases originate at the cellular level. The study of cytology has a rich history, with early discoveries made by ancient philosophers and significant contributions made by scientists throughout the centuries. Today, cytology continues to evolve with advancements in technology and techniques. It has numerous applications in various scientific disciplines, including medicine and biotechnology. By studying cytology, we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of life’s foundation and gain a deeper understanding of the wonders of the natural world.
FAQs
What is cytology?
Cytology, also known as cell biology, is the study of cells – their structure, function, and behavior.
Why is cytology important?
Cytology is important because cells are the basic unit of life. Understanding cells and their functions can help us understand how organisms function and how diseases develop.
What are the different types of cells?
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler in structure and do not have a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a nucleus.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. It controls what enters and exits the cell.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA, which controls the cell’s activities and determines its characteristics.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They produce energy in the form of ATP through a process called cellular respiration.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes are responsible for making proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells.
What is the difference between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells do not. Plant cells also have a more rigid shape, while animal cells are more flexible in shape.
Thanks for reading!
Check out ENTECH magazine at entechonline.com for articles by experienced professionals, innovators, and researchers.
Disclaimer: This blog post is not intended to provide medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or lifestyle. AI-generated images are used only for illustration and decoration. Their accuracy, quality, and appropriateness can differ. Users should avoid making decisions or assumptions based only on these images.

