Computers: Journey Ahead!
In this digital world, it is rare to find someone who doesn’t know computers. The data, as well as tools, are available in abundance. Thus, in the current age, we are facing the “Problem of Plenty”. It becomes difficult for many to access relevant information at a competent speed. The rate of technological advancements is tremendous. Teenagers, especially, face this situation very often while choosing their career or even before, i.e., deciding their area of interest. So, in this article, we explore two major aspects of the computer domain — Academics and Research, and how they shape the bold future of computer science. The academic aspect will deal with various sub-branches of Computer Science, and the Research section will discuss some emerging areas.
Background
The computer turned the 21st century into an era of technology. Computers have evolved a long way from the size of a room to as small as wearable devices. Therefore, the span is quite large, and still it is emerging. The advancements in computers are based on two major aspects: Size(reducing) and speed(increasing). Thus, this process involves a trade-off many times to maintain output efficiency at the optimum level. While dealing with computers, a student should have a short-term goal and a long-term goal, categorized as Academics and Research, respectively. Though this applies to any sector, we will be referring to the computer domain specifically.

Academics
In the Engineering stream, Computer Science branches are hot-selling today. But many sub-branches are available, and it becomes quite difficult to choose a perfect fit for an individual. In India, the following sub-branches of computers are popular and available at many Engineering institutions-
- AI (Artificial Intelligence)
- ML (Machine Learning)
- DS (Data Science)
- AI-ML
- AI-DS
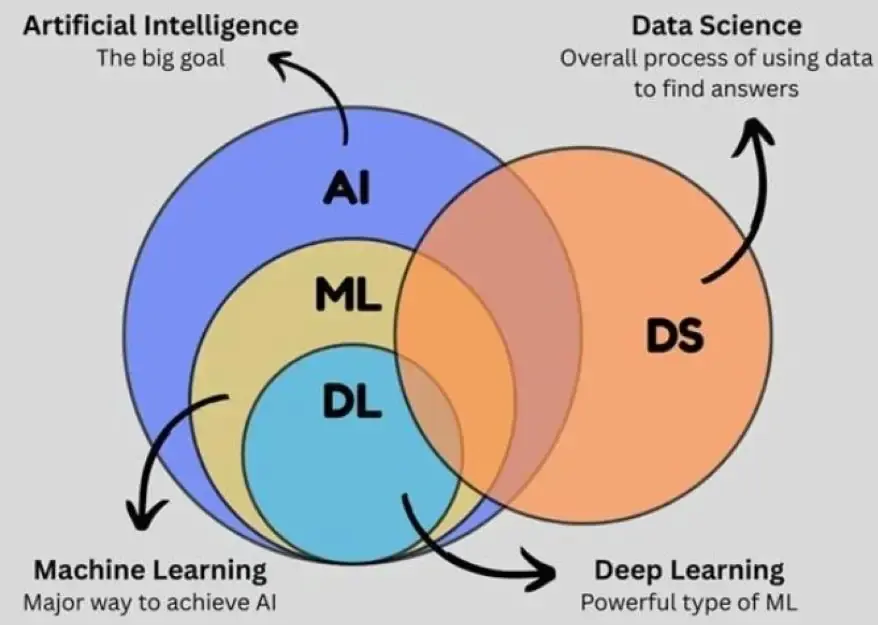
AI, ML, and DS are rather confusing terminologies that are mostly used interchangeably. Let us deal with each one separately and then with the combination.
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
It aims to create intelligent agents or systems that can reason, learn, and act autonomously. AI deals with programming machines and applications to comprehend data and take actions similar to humans. Moreover, it also involves working on challenges that lead us through suitable technological alternatives. Using AI applications, the tasks can be performed quickly and free from human error. Hence, AI assists in automation, which makes humans free to perform another task. Since the main objective of AI is to teach machines from experience, feeding the correct information and self-correction are most important.
ML (Machine Learning)
It is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Additionally, it is a narrower field that enables machines and applications to observe, study data, learn, and improve from their experience. ML algorithms identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more data.
DS (Data Science)
It is a multidisciplinary field that combines techniques from statistics and computer science to extract valuable insights and knowledge from data. DS also involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to discover patterns, make predictions, and enhance decision-making. Also, it handles enormous amounts of data generated, categorizes it, and stores it as required. It is a field of study about data systems and processes aimed at maintaining data sets and deriving meaning from them. Data science applications extract information that guides processes and helps reach end goals.
All three 3 sectors – AI, ML, and Data Science – deal with data and react differently based on information. Since these technologies are closely associated, they interlink and overlap in certain areas, with popular combinations being AI-ML and AI-DS.
AI and Machine Learning (AI-ML)
These are two interleaved subjects wherein AI grants machines the ability to simulate human behavior, while ML assists in learning the patterns with the help of previous data. It focuses on the development of smart technology that can provide an alternative for cognitive processes to understand, predict, analyze, and perform the given tasks with precision. Thus, this involves solving complex problems, developing intelligent solutions, and using data to create innovations. Also, it is particularly used to build predictive models and automate tasks.
AI and Data Science (AI-DS)
It is an interdisciplinary branch of science, engineering, and technology, creating a complete ecosystem. Certainly, it is widely used in almost every sector of the technical industry, academia, and research. But precisely, it refers to the convergence of two distinct but related fields. AI focuses on creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, while Data Science involves extracting knowledge and insights from data. It involves working with data, using specialized statistical and analytical skills, along with data-driven decisions. It emphasizes the development of data-driven solutions and tools for analyzing large datasets, incorporating machine learning and deep learning for problem-solving.
Comparison Between Various Fields in Computer Science
The sub-branches of computer science have very thin demarcations. So, it is utmost important to compare these on competent aspects. Let us consider the following comparisons.
- AI vs ML
- ML vs DS
- AI vs ML vs DS
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
| AI aims to make an intelligent computer system work like humans to solve complex problems. | ML allows machines to learn from data so they can provide accurate output. |
| AI enables a machine to emulate human behavior. | ML is a subset of AI. |
| Based on capability, AI can be categorized into Weak AI, General AI, and Strong AI. | ML can be categorized into Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. |
| AI systems are concerned with maximizing the chances of success. | ML primarily concerns accuracy and patterns. |
| Some applications of AI are virtual assistants, chatbots, intelligent humanoid robots, etc. | Applications of ML are recommendation systems, search algorithms etc. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | Data Science (DS) |
| ML helps in accurately predicting or classifying outcomes for new data points by learning patterns from historical data. | Data Science helps with creating insights from data that deals with real-world complexities. |
| Significant complexity is with the algorithms and mathematical concepts behind them. | Components for handling unstructured raw data. |
| Input data is transformed specifically for the type of algorithms used. | Most of the input data is in a human-consumable form. |
Simply put, Machine Learning is the link that connects Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, as it is the process of learning from data for a specified time. So, AI is the tool that helps DS get results and solutions for specific problems. However, ML helps in achieving that goal.
Comparison of DS, AI, and ML
Although the terms Data Science, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence are related and interconnected, each is unique and is used for different purposes.
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Data Science (DS) |
| Makes the machine work like a human. | Subsets of Artificial Intelligence. | Includes various Data Operations. |
| It combines large amounts of data through iterative processing and intelligent algorithms to help computers learn automatically. | It uses efficient programs that can use data without being explicitly told to do so. | It works by sourcing, cleaning, and processing data to extract meaning from it for analytical purposes. |
| Enables machines to perform complex tasks like humans, such as decision-making and problem-solving. | Creates a system for computers to learn from data and uses the insights to improve their operation over time. | Extracts deep insights from raw data to make informed decisions. |
| It uses logic and decision trees. | It uses statistical models. | It deals with structured and unstructured data. |
| The skills required are: Advance Maths Programming Probability & Statistics | The skills required are: Data Modelling Neural Network Natural language processing | The skills required are: Statistics Database Management Data Visualization |
| Applications are: Chatbots Voice assistants | Applications are: Recommendation Systems Facial Recognition | Applications are: Fraud Detection Healthcare analysis |
Research: Shaping the Future of Computer Science
The vast advancements in the computer field are giving rise to a diverse range of problems that need to be addressed. Thus, this invokes the research activities more predominantly. Technical research involves a systematic investigation and analysis of technical issues. Similarly, it encompasses the study of new technologies, materials, methods, and their applications across various domains. Some of the popular research areas in the computer domain are:
- Cybersecurity
- Quantum Computing
- Big data
- Robotics
- E-Commerce
Each of these areas plays a key role in shaping the future of computer science and guiding how technology will evolve.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is, nowadays matter of concern, as cyber threats and attacks are overgrowing. Attackers are now using more sophisticated techniques to target the systems. Individuals, small-scale businesses, or large organizations are all being targeted. Hence, all these firms, whether IT or non-IT firms, are concerned about cybersecurity and are focusing on adopting all possible measures to deal with cyber threats.
It is a combination of methods, processes, tools, and behavior that protect computer systems, networks, and data from cyber attacks and unauthorized access. Major challenges in this sector are increasing complexity in technology, evolving threats, and outdated strategies. One must handle it by securing multiple aspects, such as networks, information, cloud, device endpoints, applications, and operational technology.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is the field that investigates the computational power and other properties of computers based on quantum-mechanical principles. Indeed, it combines two of the most important fields of 20th-century science: quantum mechanics and computer science. Its important objective is to find quantum algorithms that are significantly faster than any classical algorithm solving the same problem. Some major advantages of quantum computing are as follows:
- Firstly, the process of reducing the size of devices has made current classical computers so powerful and cheap. This size has already reached micro-levels where quantum effects occur. Now the chip manufacturers have to suppress quantum effects to get classical behaviour. Another alternative is to try to work with them, enabling further miniaturization. Hence, utilizing quantum bits, also defined as qubits, to process data and make decisions much more quickly.
- Secondly, making use of quantum effects results in the speed-up of certain computations enormously, and even enables some things that were impossible for classical computers.
Big Data
Describes data collections that are too big and complicated for conventional data management and processing methods. The volume of data that needs to be dealt with has exploded to unimaginable levels in the past decade. At the same time, the price of data storage has systematically reduced. The challenge is to make sense of this huge data. This is where big data analytics comes into the picture.
It includes capturing data, data storage, data analysis, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Data with many cases (rows) offers greater statistical power, but higher data complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Additionally, it is high-volume, high-velocity, and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation.
Robotics
It is a branch of engineering that deals with the study of design, construction, operation, and applications of robots and intelligent machines. The primary goal of robotics is to develop intelligent machines that can assist human workers or perform low-value, repetitive tasks autonomously. Furthermore, it involves multiple engineering disciplines like mechanical engineering, electrical and electronics, computer science, control engineering, communication, and materials engineering to develop robots or autonomous machines. Robots play a vital role in accomplishing the tasks that are hazardous to people, boring, tedious, and repetitive.
Robotics helps us develop machines that can replicate human actions and perform tasks. Therefore, these machines are relatively faster, more efficient, and accurate as compared to human workers. Artificial intelligence (AI) and other cognitive technologies have recently empowered robotics to handle more complex processes and functions in different applications.
E-commerce
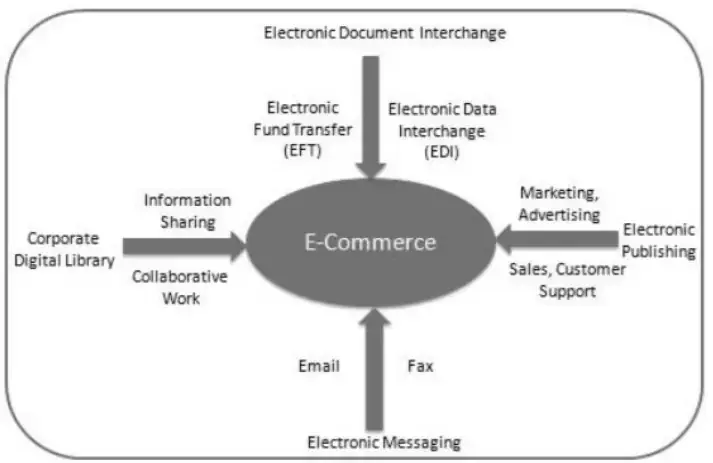
Electronic Commerce is a methodology of modern business that addresses the needs of business organizations, vendors, and customers to reduce costs and improve the quality of goods and services while increasing the speed of delivery. E-commerce refers to the paperless exchange of business information using the following ways:
- Electronic Data Exchange (EDI)
- Electronic Mail (e-mail)
- Electronic Bulletin Boards
- Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT)
- Other Network-based technologies
Using E-commerce, orders for the products can be generated anytime, anywhere, without any human intervention. It gives a big boost to existing sales volumes. It provides ways for faster, efficient, and reliable communication with customers and partners. Thus, this is made possible by the fact that e-commerce websites are hosted on the internet, which is accessible 24/7. E-commerce is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the customer experience and increase sales.
Research is an endless activity. Simultaneously, it cannot limit itself to a particular domain or sector. It’s an exhaustive process, but it may yield surprising and excellent outcomes that will benefit humanity.
Conclusion
In this article, we focused on two main aspects of the computer domain. It depends on the individual whether to go with both or restrict to academics only. Furthermore, it is difficult, though, to decide beforehand. Once you decide on the computer science branch, academics become somewhat routine activities.
But with the inclusion of NEP 2020, it has also broadened the jargon. Thus, this choice should be made with the right understanding, which is a characteristic property of a human being.
In this digital era, computers have occupied every walk of life, but the nature of usage and targeted applications vary drastically. The advancements in the computer field are at the micro level now, with popular combinations such as AI-ML and AI-DS. The research work also involves permutations and combinations of various technical areas. With the tremendous technological advancements, we are competing with machines. Hence, that’s the reason for the cut-throat competition. But humans have unique capabilities and values to withstand these situations. Happy Learning!!
References
- Fadhilah, M. (2024). Machine learning for absolute beginners. www.academia.edu. https://doi.org/10.14456/JAP.2019.25
- Gupta, N. D. V. (2023). Recent Advancements in Computer Science: A Comprehensive review of emerging technologies and innovations. International Journal for Research Publication and Seminars, 14(1), 329–334. https://doi.org/10.36676/jrps.2023-v14i1-42
- Kumar, V., & Kalil, T. A. (2015). The future of computer science and engineering is in your hands. Communications of the ACM, 58(7), 39–41. https://doi.org/10.1145/2668022
Additionally, to stay updated with the latest developments in STEM research, visit ENTECH Online. Basically, this is our digital magazine for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Furthermore, at ENTECH Online, you’ll find a wealth of information.






